- 0-Introduction
- 1-Chatbot Variables
- 2-Password IF Statements
- 3-Create Main Menu functions
- 4-Complete Quiz 3 Questions
- 5-Adding Score variable global
- 6-Debug this code
- 7-Introducing While loops Boolean flags
- 8-Introducing Validation password creation
- 9a-For Loop Guess the number
- 9b-For Loop Password Challenge
- 9c-For Loop Times table challenge
- FINAL CHALLENGE
- Skills Consolidation Task 1
- Test 1
- 0-Introduction
- 1-Introducing Lists
- 2-Personality Predictor Lists app
- 3-Players assigned weapons lists
- 3a-Nested List Matrix Snakes and Ladders game
- 3b Nested List Super Extension Complete game
- 4-String Manipulation Username Creator
- 5-StringManipulation Email Creator based on Validated username
- 6-Strip characters from password app
- 7-Create registration feature using lists
- 8-Introducing Dictionaries registration with dicts
- 8a-Course teacher finder program with dicts
- 9a-Football Club app Create and Learn
- 9b-Online Shopping Basket Checkout Program Create and Learn
- Test 1
- 0-Introduction
- 1-Introducing File Handling
- 2-READ from fake facebook file
- 3-SEARCH for username return no of friends
- 4-SEARCH by ID return full record listing
- 5-ADD WRITE a new user to file
- 6-SORT file by USER ID and Last Name
- 7-Bingo game store scores
- 8-Modulo Magic Program
- 9-Create Maths Quiz Program Tutorial
- 9a-How-to-DELETE user record row from file
- 9b-How to EDIT a field in a file
- Test 1
- 00 Intro
- 01 Main Menu Start Screen
- 02 Registration Feature Part1
- 03 Secure Password Creator
- 04 Login Functionality
- 05 MainFilms Menu Members
- 06 Allow Users to View films
- 07 Store Viewed Films by user
- 08 Allow users to like films
- 09 Search by Title
- 10 Search by Rating
- 11 Recommendations based on viewing FinalSolutions
- 00 Overview Start Here
- 01 Connect Create table
- 02 Add records to table
- 03 Fetch Display records
- 04 Update database records
- 05 Delete records
- 06 Search by condition where clause
- 07 Search for key phrase word
- 08 Sorting in SQLite
- 09 Search return selected fields
- 10 Count no rows
- 11 Find Max Value in column
- 12 Calculate Average
- 13 Calculate SUM total
- 14 Login username password sqlite
- 00-Introduction to OOP and Classes
- 01-Setup Game Canvas
- 02-Create a Ball Class
- 03-Setup main animation loop
- 04-Make the ball move up
- 05-Create bouncing ball movement
- 06-Change Starting Direction
- 07-Right left wall collision detection
- 08-Add Pong bat paddle class
- 09-Bat movement
- 10 Bat Ball collision detection
- 11 End Game Feature if ball hits bottom
- 12 Display text game over
~ OOP,Classes,Python,Tkinter ...recreating PONG
Step 5: Create bouncing ball movement
Code and Challenge
Copy and paste the code below. Run it! Read the task and see if you can do it before moving on to the next challenge
#note - an ERROR may be caused as Python is complaining about breaking out of the while loop when the window is closed - you can ignore that for now (or a fix is provied in the solutions section for those who are interested"""
"""
==========Task===============
Experiment with the bouncing angle and speed
"""
from tkinter import *
import random
import time
class Ball:
def __init__(self,canvas,color):
self.canvas=canvas
self.id=canvas.create_oval(30,30,50,50,fill=color)
self.canvas.move(self.id,100,200)
#ADD THESE LINES TO OUR __INIT__ METHOD
self.x=0 #set the object variable x to 0 (don't move the ball horizontally)
self.y=-1 #set the object variable y to -1 (this means keep moving the ball UP on initilisation)
self.canvas_height=self.canvas.winfo_height() #set the canvas height by calling the canvas function winfo_height (it gives us the current canvas height)
def draw(self): #to make the ball BOUNCE we change the draw function
self.canvas.move(self.id,self.x,self.y) #change the call to the canvas's move function by passing the object variables x and y
pos=self.canvas.coords(self.id) #create a variable called pos for position - do this by calling the canvas function coordinates
#The above function would return the current x and y coordinates of anything drawn on the canvas as long as you know the identifying number
#In this case it is the oval's identifier (self.id) that gives us the coordinates
""" About the Coordinates
1. coords function returns the coordinates as a list of four numbers
[a,b,c,d] (e.g. 255,20,280,50)
First two numbers = top left coordinates of the oval that are x1 and y1
Last two numbers = bottom right x2 and y2 coordinates
"""
if pos[1] <=0: #if you hit the top of the screen then stop subtracting 1 as defined in the __init__ method and therefore stop moving up -reverse directions
self.y=1
if pos[3] >=self.canvas_height: #if the bottom coordinates are greater or equal to canvas height, then reverse again, and set y back to -1 (go up)
self.y=-1
def main():
tk=Tk()
tk.title("My 21st Century Pong Game")
tk.resizable(0,0)
tk.wm_attributes("-topmost",1)
canvas=Canvas(tk,bg="white",width=500,height=400,bd=0,highlightthickness=0)
canvas.pack()
tk.update()
ball1=Ball(canvas,'green')
while 1:
tk.update()
ball1.draw() #call the ball draw method here
time.sleep(0.01)
main()
Code your solution here
Systems Life Cycle (in a nutshell): Analyse - Design - Create - Test - Evaluate. Designing something or writing out some pseudocode before you actually write code is always a good idea! Get in to the habit of doing so! You can draw your flowchart here and screenshot it.A sample flow chart (design) for this particular challenge could look like:
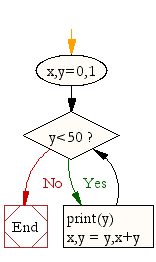
Each challenge section below provides an online drawing tool where you can dynamically create flowcharts. Screenshot them into your presentation for submission.
Solutions & Answers
Answers /Solutions in the "members area" drive under: "Solve and Learn >>SOLUTIONS"Testing Table
You may want to read a little about Testing first. A teacher may go through some examples with you. Feel free to fill in the test table here, and screenshot it in to your powerpoint. Testing is absolutely essential once you have created a program!| Test No. | Description | Test Data(input) | Expected Outcome | Actual Outcome | Further Action? |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | |||||
| 2 | |||||
| 3 | |||||
| 4 | |||||
| 5 |
Coming soon!