Preview lessons, content and tests
Computer Science & Programming solved. All in one platform.
1. To trial the platform and take tests, please take a few seconds to SIGN UP and SET UP FREE.2. Searching for something specific? See our text overview of all tests. Scroll right for levels, and lists. 3. Student and Teacher User Guides | Schemes of Work | Real Teacher use Videos |
Join 36000+ teachers and students using TTIO.
Linear or Sequential Search
In computer science, linear search or sequential search is a method for finding a target value within a list. It sequentially checks each element of the list for the target value until a match is found or until all the elements have been searched.[1]
Linear search runs in at worst linear time and makes at most n comparisons, where n is the length of the list. If each element is equally likely to be searched, then linear search has an average case of n/2 comparisons, but the average case can be affected if the search probabilities for each element vary. Linear search is rarely practical because other search algorithms and schemes, such as the binary search algorithm and hash tables, allow significantly faster searching for all but short lists
Suggested Video
How to code a Linear search
A step by step implementation of coding a linear search in python
Challenge
#1 Write a Python program to search using the sequential/linear search method
#2 Comment each line of the python solution below to show your understanding of the algorithm
Try it yourself
Solution
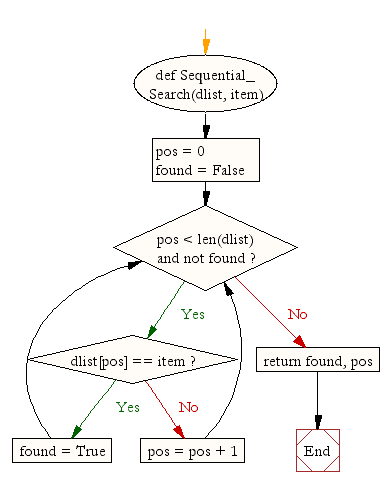
def Sequential_Search(dlist, item):
pos = 0
found = False
while pos < len(dlist) and not found:
if dlist[pos] == item:
found = True
else:
pos = pos + 1
return found, pos
print(Sequential_Search([11,23,58,31,56,77,43,12,65,19],31))
Flowchart
Visualisations and animations
https://www.hackerearth.com/practice/algorithms/sorting/insertion-sort/visualize/