Preview lessons, content and tests
Computer Science & Programming solved. All in one platform.
1. To trial the platform and take tests, please take a few seconds to SIGN UP and SET UP FREE.2. Searching for something specific? See our text overview of all tests. Scroll right for levels, and lists. 3. Student and Teacher User Guides | Schemes of Work | Real Teacher use Videos |
Join 36000+ teachers and students using TTIO.
FQDN
A fully qualified domain name (FQDN), sometimes also referred to as an absolute domain name, is a domain name that specifies its exact location in the tree hierarchy of the Domain Name System (DNS). It specifies all domain levels, including the top-level domain and the root zone. A fully qualified domain name is distinguished by its lack of ambiguity: it can be interpreted only in one way. It usually consists of a host name and at least one higher-level domain (label) separated by the symbol "." and always ends in the top-level domain.
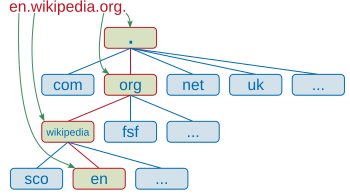
The hierarchy of labels in a fully qualified domain name (Above)
Domain Name
A domain name is an identification string that defines a realm of administrative autonomy, authority or control within the Internet. Domain names are used in various networking contexts and for application-specific naming and addressing purposes.
Use in web site hosting
The domain name is a component of a uniform resource locator (URL) used to access websites, for example:
- URL: http://www.example.net/index.html
- Top-level domain: net
- Second-level domain: example
- Hostname: www
IP Address
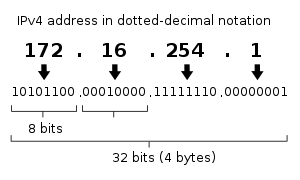
An Internet Protocol address (IP address) is a numerical label assigned to each device connected to a computer network that uses the Internet Protocol for communication. An IP address serves two main functions: host or network interface identification and addressing.
Video: DNS Explained
Video: IP Addresses
Discussion
Read this article. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/IPv4_address_exhaustion
What are your thoughts on the future of IP addresses? Can you think of an alternative solution to the one that has been proposed? https://tech.slashdot.org/story/14/02/17/1319204/whatever-happened-to-the-ipv4-address-crisis
Additional Reading and Resources