Preview lessons, content and tests
Computer Science & Programming solved. All in one platform.
1. To trial the platform and take tests, please take a few seconds to SIGN UP and SET UP FREE.2. Searching for something specific? See our text overview of all tests. Scroll right for levels, and lists. 3. Student and Teacher User Guides | Schemes of Work | Real Teacher use Videos |
Join 36000+ teachers and students using TTIO.
Insertion Sort
Insertion sort is a simple sorting algorithm that builds the final sorted array (or list) one item at a time. It is a comparison-based algorithm that builds a final sorted array one element at a time. It iterates through an input array and removes one element per iteration, finds the place the element belongs in the array, and then places it there.
Suggested Video
It is generally considered much less efficient on large lists than more advanced algorithms such as quicksort, heapsort, or merge sort although it does has its own advantages - see additional information below.
Challenge
#1 Write a Python program to sort a list of elements using the Insertion sort algorithm
#2 Comment each line of the python solution below to show your understanding of the algorithm
Try it yourself
Solution
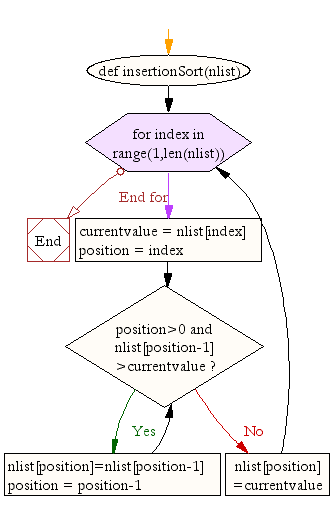
def insertionSort(nlist):
for index in range(1,len(nlist)):
currentvalue = nlist[index]
position = index
while position>0 and nlist[position-1]>currentvalue:
nlist[position]=nlist[position-1]
position = position-1
nlist[position]=currentvalue
nlist = [14,46,43,27,57,41,45,21,70]
insertionSort(nlist)
print(nlist)
Animated Demo

Flow Chart
Additional Information
Insertion sort provides several advantages:
- Simple implementation: Jon Bentley shows a three-line C version, and a five-line optimized version
- Efficient for (quite) small data sets, much like other quadratic sorting algorithms
- More efficient in practice than most other simple quadratic (i.e., O(n2)) algorithms such as selection sort or bubble sort
- Adaptive, i.e., efficient for data sets that are already substantially sorted: the time complexity is O(nk) when each element in the input is no more than k places away from its sorted position
- Stable; i.e., does not change the relative order of elements with equal keys
- In-place; i.e., only requires a constant amount O(1) of additional memory space